Filtration (dewatering) of highly dispersed suspensions (pulp):
Copper flotoconcentrates
Cobalt
Nickel
Lead
Tin
Magnetite
Apatite
Talc, etc
Price on request
Working principle:
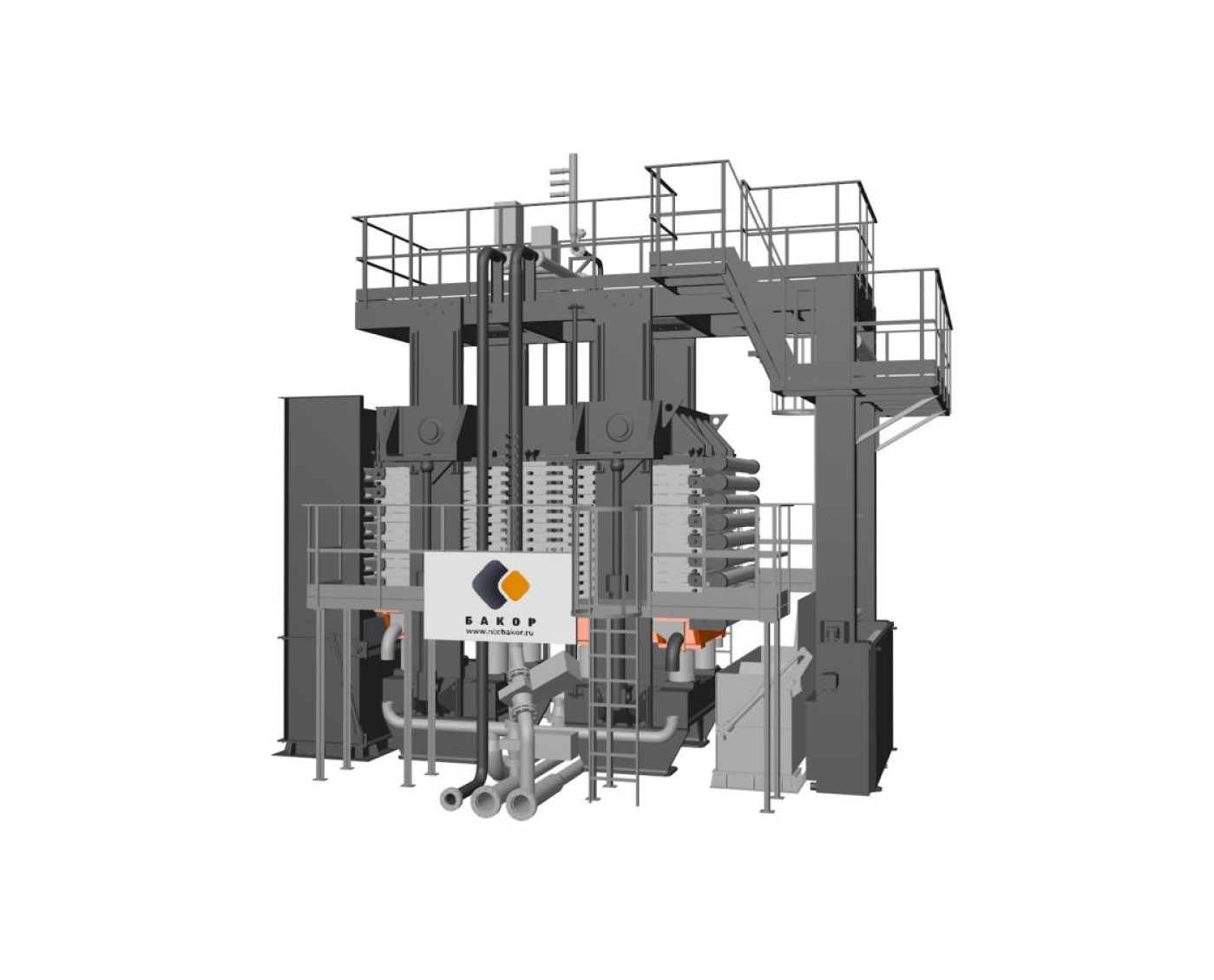
Filtration (separation of suspensions into two phases - liquid and solid). The press filter is a cyclic action technological unit, the main element of which is a package of filter plates mounted on a frame.
Objects of application:
The filters are used to filter a wide range of suspensions, and they are also suitable for separation of suspensions with a small concentration of solid particles and suspensions with elevated temperature, the cooling of which is inadmissible due to the precipitation of crystals from the liquid.
Advantages:
Efficiency:
Performance, kg/m2*h | Solid phase content, % | Moisture, % | Material |
350 | 9,5-10,5 | Cu-Ni concent. | |
830-850 | 7,5 | Zn concent. | |
90 | 20 | Zn leaching sludge | |
72 | 20 | ZnO leaching sludge | |
100 | 17-21 | Zn leaching sludge | |
230 | 12,5 | Cu concent. | |
320 | 14 | Talc | |
90 | 15-20 | Scrubber sludge Pb Zn sulfides | |
200 | 150÷300 г/л | 19÷22 | 4A-zeolite |
250÷280 | 50% | 7÷8 | sulfur concent |
120 | 50% | 30 | sulfur melt |
35 | 50% | 15÷20 | melts of lead compounds |
320 | 600 г/л | 8÷9 | copper smelting slags |
100÷150 | 5%÷10% | 28÷35 | calcium sulfate in wastewater |
200÷250 | 40% | 14÷18 | gold bearing rock waste |
23÷69 | 15%÷20% | 29÷32 | ultrafine aluminum hydroxide |
360 | 50%÷65% | 9,78 | copper-nickel concentrates |
300÷400 | 45%÷50% | 7,6 | copper concentrates |
200 | 45%÷50% | 8 | nickel concentrates |
122÷150 | 10% | 20÷25 | tantalum-niobium melts |
300 | 10% | 11,3 | K-acids |
280 | 30%÷35% | 16÷17 | coal slimes |
300 | 40% | ≤9 | iron slags |
220 | 20%÷30% | 12÷18 | gold flotation waste |
160÷180 | 30% | 32 | modified starch |
90 | 12 | mannitol | |
72 | 57% | 20 | zinc oxide powder |
257 | 50,50% | 18÷20 | zinc residue leaching |
65÷75 | 50% | 30÷40 | arsenic sulfide |
200÷220 | 30% | 32 | starch |
Main technological stages of filtration:
1. Filtration
The process slurry is pumped simultaneously into all filter chambers. A sluge begins to form while the filtrate is displaced by the next slurry entering the chamber. As the cake forms, the injection pressure is increased and the filtrate is forced through the fabric until the desired cake thickness is reached.
2. Pressurization
High-pressure water or air automatically fills the supradiaphragm space at the top of each chamber, reducing chamber volume and compressing the cake to remove more filtrate. This cake filtration process and tightly woven filter cloth results in exceptionally clean filtrate, with high pressure maximizing filtration efficiency. Diaphragm squeezing produces a homogeneous dewatered cake of uniform thickness with minimal residual moisture, which facilitates water washing and air blowing.
3. Cake flushing (optional).
Flushing fluid is fed through the slurry pipe to flush the solid cake, removing dissolved solids from the cake.
4. Re-pressing. (optional)
Re-pressing forces the washing liquid evenly through the cake layer and removes it.
5. Blowing with air
Compressed air is blown through the cake for final dewatering. The moisture content is minimized. This process can be very precisely controlled by varying the pressure and duration of the blowing.
6. Unloading the cake and rinsing the fabric
After opening the plate pack, the dewatered cake is removed from each chamber by means of a movable filter cloth. An integrated high pressure rinsing unit sprays liquid on both sides of the cloth, minimizing clogging and ensuring uniform filtration.
Name / Characteristics | Total filtering area, m2 | Number of chambers, pcs. |
|---|---|---|
BPF-100 (rus. БПФ-100) | 100 | 14 |
BPF-85 (rus. БПФ-85) | 85 | 12 |
BPF-70 (rus. БПФ-70) | 70 | 10 |
BPF-55 (rus. БПФ-55) | 55 | 8 |
Labeling:
БПФ Tower press filter (Башенный пресс-фильтр)
БПФ-100 filtering area, m2
Equipment Options:
1. Sensors:
Strain gauges | Cake weight |
Pressure sensors | Feed, press, cake wash, fabric wash, hydraulic system. |
Position sensors | Hydraulic cylinder displacement, fabric position, fabric displacement |
Flow meters | Feed, air, water, filtrate. |
Turbidity meter (turbidimeter) | Filtrate turbidity |
Temperature sensors | Fluids and air |
Density meter | For regulating the height of the cake |
2. Tank for separation of air and filtrate.
3. pulp preparation tank with agitator
4. Pumping equipment
5. Compressor station